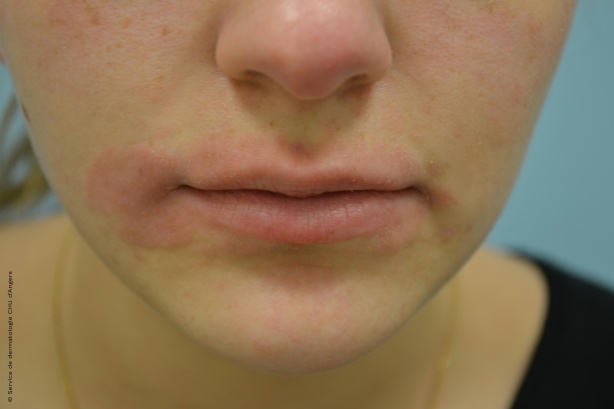
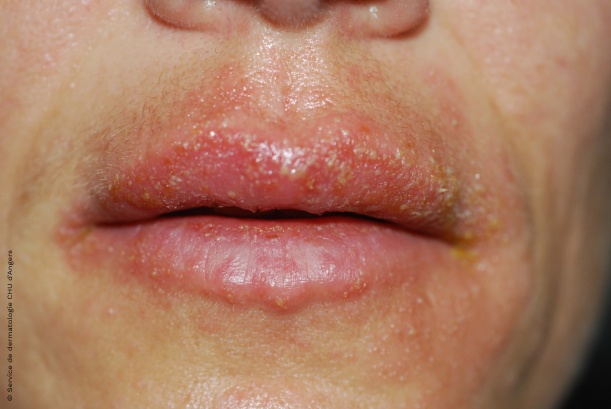
Eczema around the mouth

The condition is characterized by scabs and oozing in cases of acute eczema.
The best habits for providing soothing relief from eczema depend on its root cause: allergic or atopic?
Allergic eczema or atopic eczema?
Contact eczema: an allergy
Is the eczema affecting other parts of the body besides the area around the mouth? Do you have a history of atopy? If you answered no to both these questions, it is likely allergic eczema. You may develop a sudden allergy to a product at any point throughout your life, even if you have already handled or used it before, an allergy which manifests as eczema.
Contact with the allergen may be direct, as with an allergic reaction to a cosmetic applied to the face for example, or it can occur indirectly, especially via the hands, which often touch the mouth. For example, you may be allergic to a nail polish or to a product you touched beforehand.
Products or objects commonly known to trigger eczema around the mouth include:
- lip sticks and lip balms (fragrances, Balsam of Peru, etc.)
- nail polish (formol derivatives)
- cosmetics
- medications
- toothpaste (essential oils)
- dental solutions
- musical instruments
- etc.
Several weeks can pass from the point of initial contact and the reaction, making it difficult to find the culprit. It is always recommended to consult a doctor, who will help confirm the cause by carrying out allergy tests (or by asking several questions about your lifestyle habits in order to fine-tune the tests). They will also be able to tell you what products contain the allergen. If you have an allergic reaction to formaldehyde in a cosmetic, for example, you will need to avoid this product as well as any others that contain formaldehyde.
Atopic eczema: hypersensitivity to the environment
Atopic skin is hypersensitive to certain environmental factors (animal hair, pollen, etc.). This condition is hereditary and can manifest in different ways: as eczema, asthma or even rhinitis.
In the case of atopic eczema, this hypersensitivity to the environment affects the skin, causing it to over-react. Skin becomes inflamed during flare-ups, which alternate between periods of remission.
Unlike an allergic reaction, atopic eczema is rarely limited to a single area. If you have it on your face, chances are you have it on the crook of the arms as well. This would point to atopic eczema.
How to provide soothing relief from eczema around the mouth
Contact eczema
When eczema is caused by an allergic reaction, you should avoid further exposure to the allergen simply by eliminating it from your daily routine.
For flare-ups, your doctor will prescribe a topical corticosteroid to soothe itching and treat eczema.
Atopic eczema
On the one hand, you need to soothe the skin (like a firefighter), and on the other hand, you need to repair it (like a mason). To soothe the skin, use a topical corticosteroid during flare-ups. To repair it, apply an emollient to hydrate skin regularly and prevent flare-ups.
Can stress cause eczema around the mouth?
This is one of the most common misconceptions about eczema. However, stress is never the cause of eczema. The actual cause is either an allergy or atopic skin. Stress can play a secondary role, for example as a trigger for flare-ups. But strictly speaking, eczema has no psychological cause.
What are the differences between psoriasis and eczema?
People often confuse the two, but when you look closely, they have some differences: psoriasis patches are thicker and their edges more defined compared to eczema. Click here for a summary on the differences between eczema and psoriasis, with photos.